China Fast Food Market Share
The fast food industry in China has become one of the most vital sectors in the nation’s broader foodservice industry, experiencing rapid growth over the past few decades. As of 2024, the market size is estimated at over USD 70 billion, with an expected annual growth rate ranging from 8 to 10%. Several factors drive this expansion, including rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and the increasing demand for convenience and affordability in food. Additionally, the younger generation’s changing lifestyle, which places a premium on speed, variety, and novelty, has provided fertile ground for the fast food market to flourish. This landscape has seen the dominance of both international and local players, with each adapting strategies to meet the evolving tastes and preferences of Chinese consumers.
China’s market is unique compared to other global fast food markets, with the blend of international brands and homegrown chains that reflect the country’s diversity, culture, and fast-paced lifestyle. As the industry continues to grow, these players are also adjusting to new consumer expectations, such as healthier menu options, environmental sustainability, and tech-driven experiences like online ordering and delivery services. In this article, we’ll explore the key players in China’s fast food market, their strategies, and the ongoing trends that are shaping the market landscape.
Major Players in the Chinese Fast Food Market
International Chains
McDonald’s
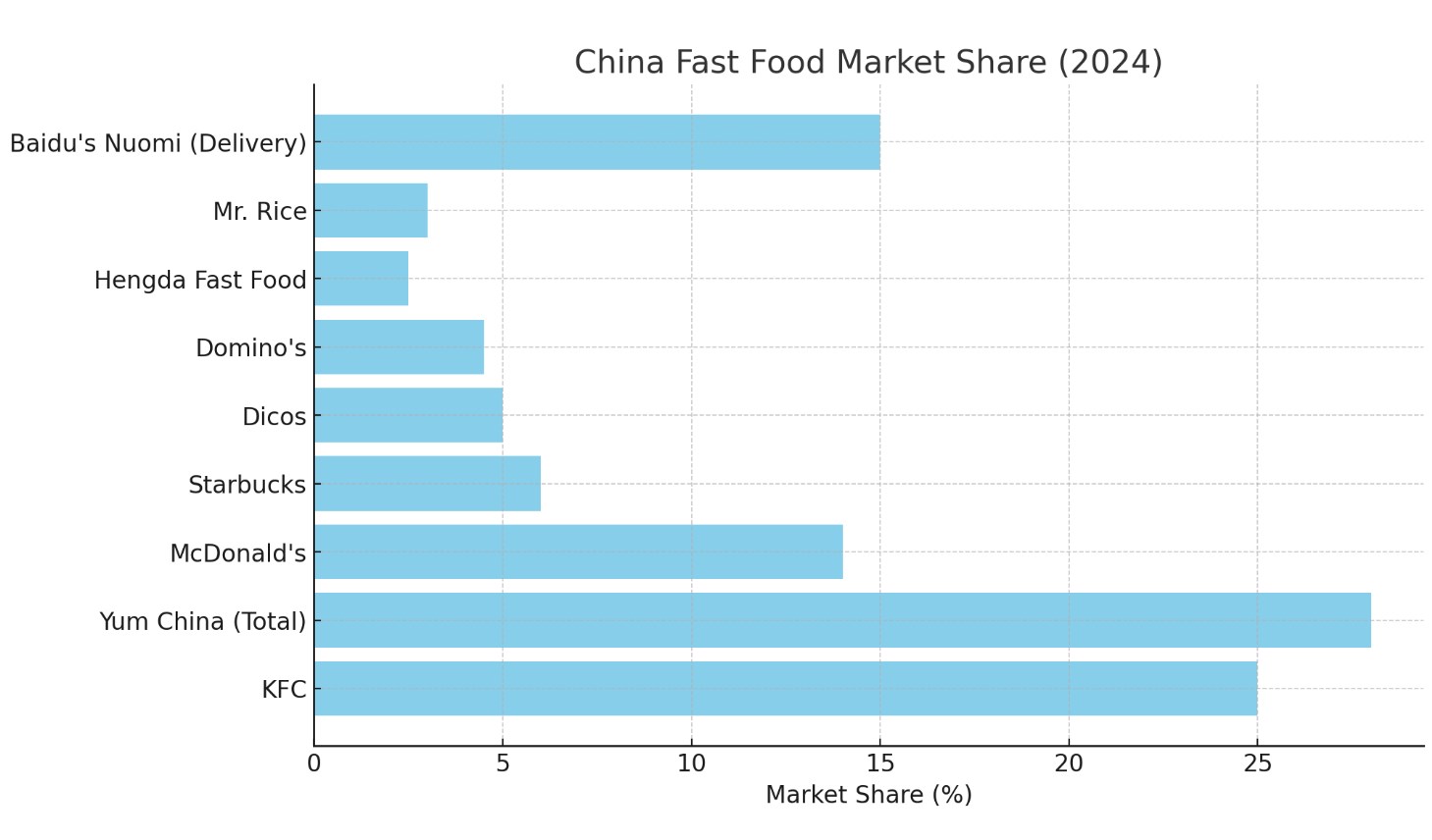
McDonald’s has long been one of the most prominent international fast food brands in China, with a significant market share of around 14%. This translates to approximately USD 9.8 billion in annual revenues. The American brand’s success in China is largely due to its strategic localization efforts, where McDonald’s has consistently adapted its menu to cater to the Chinese palate. Special offerings such as the “Spicy McChicken” and “Taro Pie” have been well-received by local consumers, and the introduction of breakfast items such as “Congee” has further ingrained McDonald’s into Chinese dining habits. The company’s expansion into delivery services, through partnerships with local platforms like Meituan and Ele.me, has also boosted its reach, particularly in major cities like Beijing and Shanghai.
Moreover, McDonald’s continues to experiment with new menu items, such as vegetarian options, as part of its strategy to meet the growing demand for healthier food choices in the Chinese market. Additionally, McDonald’s has embraced digital ordering and drive-thru services, which resonate with the urban population that seeks quick and efficient service. The company’s focus on quality, innovation, and customer experience has allowed it to maintain a robust presence in one of the most competitive fast food markets in the world.
KFC
KFC has been operating in China since the early 1990s and has managed to build a dominant market position, holding roughly 25% of the total fast food market share. This dominance translates to a staggering USD 17 billion in annual revenue. KFC’s success is primarily due to its deep understanding of Chinese food culture and its ability to localize its offerings. The brand has become a cultural staple, not just as a fast food option but as a place for families to gather and enjoy affordable meals.
KFC has mastered the art of localization by introducing unique Chinese menu items, such as congee (rice porridge), Chinese-style dumplings, and even tea-infused desserts. In addition to its localized menu, KFC has developed a strong regional presence across China’s vast landscape, with stores in both tier-one and tier-two cities. The company has also expanded its product lines to include healthier options, like salads and grilled chicken, to cater to a growing health-conscious consumer base.
Furthermore, KFC has embraced technology with a robust mobile app and delivery options, which has expanded its reach in the online food delivery market. In recent years, the company has focused heavily on enhancing its digital infrastructure, offering consumers the convenience of ordering food from the comfort of their homes or offices, which has become particularly popular in urban centers.
Starbucks
Starbucks, while primarily known for its coffee offerings, has become a key player in China’s broader fast food market by targeting consumers looking for quick, light meals and beverages. In 2024, Starbucks holds a 6% market share, which translates to over USD 4.5 billion in revenue from its operations in China. The brand has capitalized on China’s growing middle class, particularly in large cities like Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou. Starbucks’ appeal lies not only in its coffee but also in its ability to provide an upscale, modern cafe experience that resonates with younger, affluent consumers.
Starbucks’ success in China can be attributed to its deep localization efforts. The company has introduced Chinese-specific beverages, such as the Matcha Latte and Red Bean Frappuccino, to cater to local tastes. Additionally, seasonal offerings like Mooncakes during the Mid-Autumn Festival and Chinese New Year specials have helped Starbucks integrate into Chinese cultural traditions. The brand has also incorporated Chinese flavors into its food menu, offering savory options like dim sum and egg tarts, which appeal to local preferences.
Moreover, Starbucks has expanded its delivery services in partnership with food delivery platforms such as Meituan and Ele.me, making it easier for customers to enjoy Starbucks products from the convenience of their homes. The company continues to innovate, with the introduction of smart coffee machines and its digital loyalty programs that encourage repeat business.
Domino’s Pizza
Domino’s Pizza has emerged as a serious contender in China’s fast food industry, especially in urban areas. The brand is experiencing notable growth in the market, where it holds around 4.5% of the total fast food market share, equating to over USD 3 billion in revenue. Domino’s success lies in its ability to localize its menu to fit the preferences of Chinese consumers. For example, it has introduced regional toppings like sweet corn, shrimp, and hotpot-style sauces to appeal to local tastes.
Domino’s has also taken advantage of the growing demand for home delivery, a trend that has been reinforced by the rise of online food delivery apps. The company has been quick to implement efficient, fast delivery systems to meet the needs of busy urbanites. With its focus on affordability, quality, and fast service, Domino’s is likely to continue expanding its footprint in China’s increasingly competitive fast food market.
Domestic Chains
Dicos
Dicos is one of the largest homegrown fast food chains in China, often seen as a competitor to KFC due to its similar offerings. As of 2024, Dicos holds approximately 5% of the market share, generating over USD 3.5 billion in revenue. The company has been particularly successful in tier-two and tier-three cities, where it appeals to consumers looking for affordable, fast meals that are locally inspired. Dicos’ menu includes chicken sandwiches, fried chicken, and Chinese breakfast foods like soy milk and fried dough sticks.
Dicos has distinguished itself by offering value for money and expanding its operations in less saturated markets, which has allowed the brand to capture a significant portion of the domestic fast food sector. The chain has also embraced technological innovations, such as mobile ordering and self-service kiosks, which enhance the customer experience and reduce wait times.
Yum China
Yum China, the operator of KFC and Pizza Hut in China, is a powerhouse in the Chinese fast food market, commanding a significant share of nearly 28%. In 2024, its revenue exceeds USD 19 billion, driven by the combined success of KFC, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell, and various other fast casual dining brands. Yum China is unique in its ability to leverage the success of established international brands while also expanding into new segments with products tailored to Chinese consumers.
The company has been adept at offering localized versions of international menu items. KFC, for instance, serves hot pot dishes and rice bowls, which are integral to Chinese dining culture. Pizza Hut, while still offering traditional Western-style pizzas, has diversified its menu to include rice-based dishes, local-style appetizers, and desserts. Additionally, Yum China has been actively expanding its presence in second- and third-tier cities, where rising middle-class populations and changing consumption habits are driving demand for both Western and local fast food.
Baidu’s Nuomi (Online Delivery Platform)
While not a fast food chain in itself, Baidu’s Nuomi platform has become a key player in the Chinese fast food market by facilitating online food delivery. The growth of food delivery services has fundamentally altered the way Chinese consumers access fast food, with companies like Baidu partnering with local restaurants and chains to streamline the ordering process. Nuomi, along with competitors like Meituan and Ele.me, now accounts for a significant portion of fast food sales, particularly in urban areas. By the end of 2024, food delivery platforms are expected to account for 15% of the total fast food market share in China.
Local Fast Casual Chains
Hengda Fast Food
Hengda Fast Food is a rapidly growing domestic chain that focuses on offering affordable, healthy Chinese-style fast food. The brand specializes in stir-fried rice, rice bowls, and noodle soups, which have become favorites among office workers and students. Hengda has successfully targeted a growing health-conscious demographic in China’s second-tier cities, offering meals that balance convenience with nutrition. By 2024, Hengda is expected to capture around 2.5% of the market share, translating to revenues of over USD 1.7 billion.
Mr. Rice
Mr. Rice is another notable player in China’s fast food market, specializing in rice-based meals that cater to the preferences of local consumers. The brand has focused on offering quick, affordable meals with a focus on rice, which is a staple in Chinese cuisine. Mr. Rice has gained traction due to its variety of options, including stir-fried rice, rice bowls, and hot pot, and its emphasis on speedy service. By the end of 2024, Mr. Rice is expected to hold a 3% market share, translating to USD 2.1 billion in revenue.
Key Trends Shaping the Market
Localization and Menu Innovation
Localization has been a key factor in the success of both international and domestic fast food chains in China. Brands like McDonald’s, KFC, and Domino’s have recognized the importance of offering menu items that align with Chinese tastes. McDonald’s has introduced unique items like the “Green Tea McFlurry” to cater to local tastes, while KFC’s Chinese breakfast options, including congee, have helped the brand build a loyal following. Similarly, local chains like Hengda and Mr. Rice have thrived by offering dishes that resonate with Chinese consumers, emphasizing the importance of food that is both convenient and culturally relevant.
Digital Transformation and Delivery Services
The rise of online food delivery platforms, such as Meituan, Ele.me, and Baidu’s Nuomi, has reshaped the fast food market in China. Consumers are increasingly opting for the convenience of having food delivered to their doorsteps, leading to a surge in demand for online ordering and delivery services. Brands have adapted by integrating these platforms into their business models, offering promotions, discounts, and loyalty programs to drive orders.
Health Consciousness and Menu Diversification
As Chinese consumers become more health-conscious, the fast food industry has shifted towards healthier offerings. Brands are introducing low-calorie meals, grilled options, and plant-based alternatives to cater to this demand. Additionally, there is a growing focus on environmental sustainability, with companies exploring eco-friendly packaging and reducing food waste.
Rising Competition and Mergers & Acquisitions
China’s fast food market is seeing heightened competition, with both international and domestic brands vying for market share. Mergers and acquisitions are becoming more common as companies look to expand their reach, diversify their portfolios, and enhance their competitive position. Brands are investing in innovations such as healthier menu items, digital ordering platforms, and improved delivery systems to stay ahead in the fast-paced and ever-evolving Chinese market.
